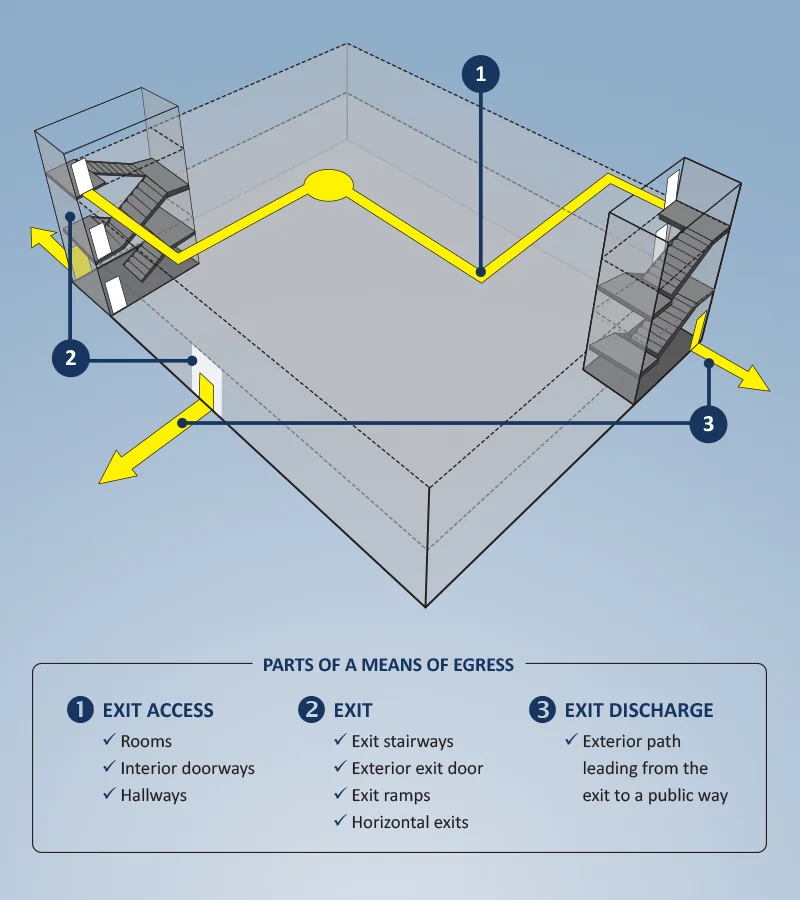
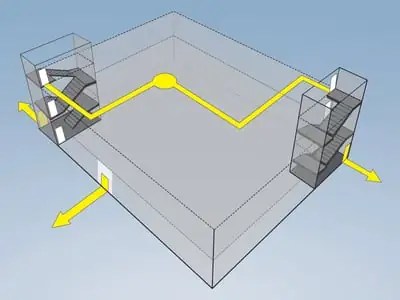
A means of egress is the path of travel from the building to the outside. It is the emergency escape route in case of fire or other emergency and includes the fire exits, stairs, and walkways that allow occupants to exit the building. To define means of egress we will explore the different parts of the means of egress and provide example diagrams for different types of egress.
Means of egress definition in construction
The means of egress definition in construction is the same as for any building occupancy. A means of egress is a continuous and unobstructed path of vertical and horizontal egress travel from any occupied portion of a building to a public way, such as a street or parcel of land.
OSHA section 1926.34 defines the requirements for means of egress in construction.
1926.34(a) In every building or structure exits shall be so arranged and maintained as to provide free and unobstructed egress from all parts of the building or structure at all times when it is occupied. No lock or fastening to prevent free escape from the inside of any building shall be installed except in mental, penal, or corrective institutions where supervisory personnel is continually on duty and effective provisions are made to remove occupants in case of fire or other emergencies.
1926.34(b) Exits shall be marked by a readily visible sign. Access to exits shall be marked by readily visible signs in all cases where the exit or way to reach it is not immediately visible to the occupants.
1926.34(c) The means of egress shall be continually maintained free of all obstructions or impediments to full instant use in the case of fire or other emergency.
Means of Egress Diagram |
 |
Design requirements for a means of egress are established according to IBC chapter 10. This chapter defines the requirements for the number of exits, the width of exit stairways, exit signs, travel distance, and other important design factors to ensure a safe egress system.
The exit discharge is the part of the means of egress that leads from the exit, such as the stairway, to the public way. The exit discharge is usually an exterior path of egress travel between the building and the public way.
Means of egress examples
Means of egress diagrams can help better understand how the egress system is used and how each part works together to form a safe exit route from the building in case of emergency.
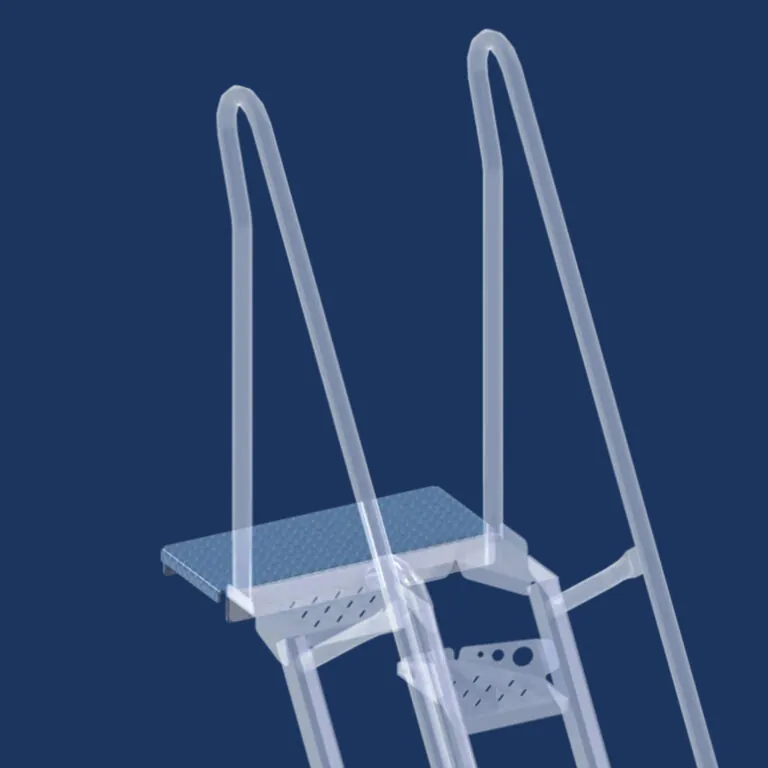
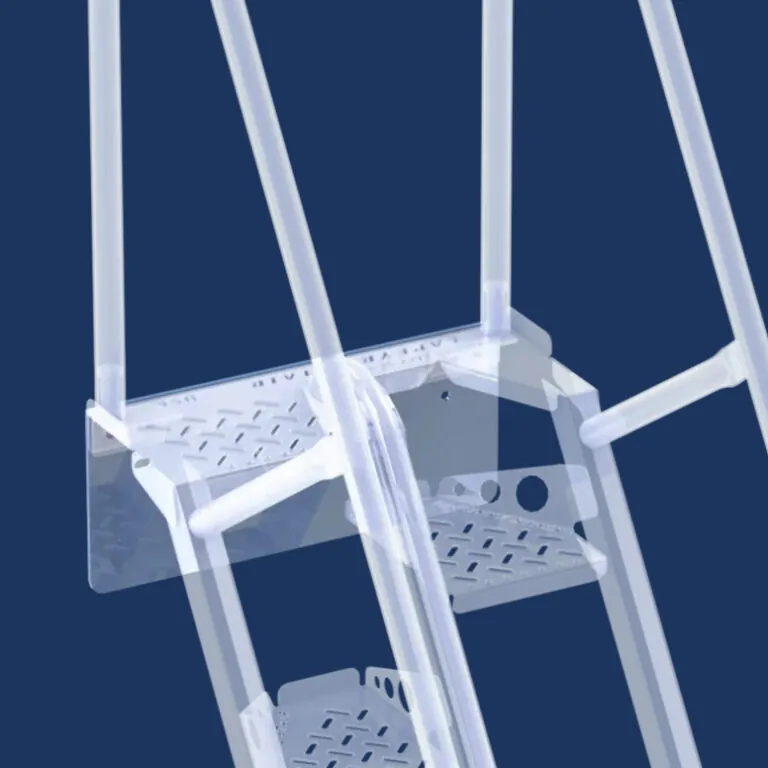
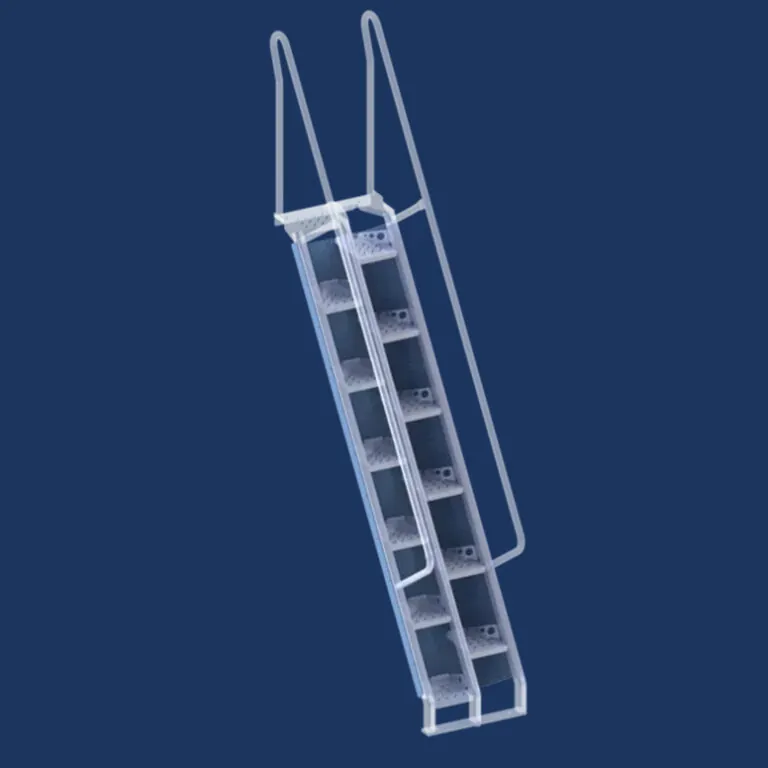
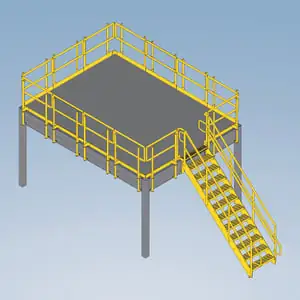
Mezzanine egress example diagram
A mezzanine is an intermediate level or levels in a building between the floor and the ceiling of any story within the building. While a mezzanine is often a separate structure from the main building, in determining the mezzanine egress requirements, the mezzanine level is considered part of the story below it within the building. Because it is part of the story below it, the mezzanine must have a means of egress complying with IBC Chapter 10.
The mezzanine means of egress usually consists of a mezzanine stairway complying with the IBC code requirements for industrial stairs.

Roof egress example diagram
A means of egress from the roof must be provided to allow safe exit from the roof. The requirements for the means of egress depends on whether the roof is occupied or unoccupied. Occupied roofs must be provided with an egress stairway like any other occupied portion of the building. The unoccupied roof egress requirements allow an exception since the roof will not be occupied by the general public.
For unoccupied roofs, under the exception to IBC 1011.12, access to the roof from the top story is permitted to be by an alternating tread device, a ships ladder, or a permanent ladder.
Also, the exception to IBC 1011.12.2 allows access to unoccupied roofs to be a roof hatch or trap door. So for unoccupied roofs, a ladder or alternating tread stair extending through a roof hatch is the most common method of accessing the roof.
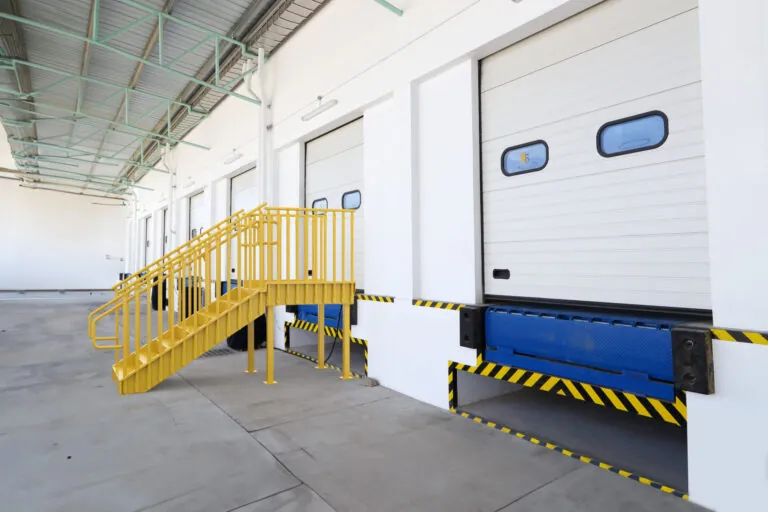
Commercial egress example diagram
 The commercial egress requirements are established by the International Building Code (IBC), the National Fire Protection Agency Life Safety Code (NFPA), and the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). Your local building code will adopt one or more of these standard under the IBC and NFPA. The ADA requirements are federally enforced and all local building codes will need to comply.
The commercial egress requirements are established by the International Building Code (IBC), the National Fire Protection Agency Life Safety Code (NFPA), and the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). Your local building code will adopt one or more of these standard under the IBC and NFPA. The ADA requirements are federally enforced and all local building codes will need to comply.
A commercial means of egress consists of the exit access, the exit, and the exit discharge. Generally, every building must have at least two means of egress. The minimum size and widths of the means of egress are calculated according to IBC Section 1005.
The exit access is the portion that leads from the occupied are to the exit. This can be a hallway, passageway, or access door.
The exit is the portion between the exit access and the exit discharge. Examples of exits are exterior exit doors, interior egress stairs, ramps, exterior fire escape stairs, and horizontal exits. The number of exits required depends on the building occupant load or the number of occupants per unit of floor area within the building.
The exit discharge is the portion that leads from the exit to the public way. An example of an exit discharge is an exterior walkway leading from the exit door to the street.
Exterior egress diagram example
Exterior egress is the portion of the means of egress located on the exterior of the building. Examples of exterior egress are exterior egress stairs, exterior ramps, courtyards, and exterior walkways.
Exterior egress stair requirements are established by IBC in sections 1027 for exterior stairways.
Final points
A means of egress is a critical system of any building so that occupants can safely exit in case of emergency. Every building should have adequate means of egress designed according to the building code and life safety requirements.
FAQ
What does means of egress mean?
Means of egress means the path of travel from any occupied portion of a building to a public way, such as a street or parcel of land. It is the emergency escape route in case of fire and includes the fire exits, stairs, and walkways used to exit the building.